New Resources for Mumps
Jennifer Chang, Richard Neher, Jover Lee, Kim Andrews
Expanding the collection of core pathogen datasets, we now provide regularly updated phylogenetic monitoring of mumps virus at:
These phylogenies are generated using genomic data from NCBI GenBank, and are updated daily when new sequences are uploaded to NCBI.
# Phylogenetic analysis
Mumps orthorubulavirus causes mumps, a viral disease spread primarily among humans that is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets. The virus typically infects the salivary glands, causing characteristic swelling and inflammation, making it difficult to speak or move the jaw. The occurrence of mumps infections has been reduced by the widespread use of the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine.
We provide two views of mumps for genomic analysis, a Global and a North-America filtered dataset.
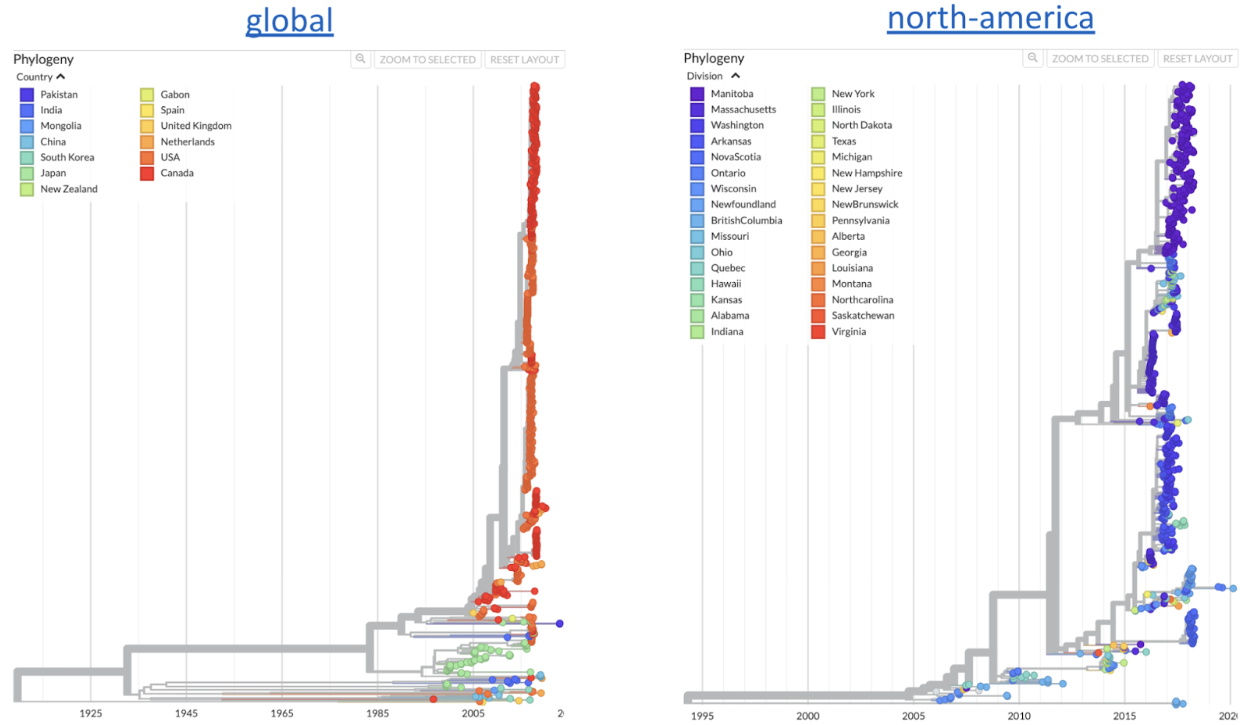 Figure 1. Phylogenetic views of mumps viral genetic diversity. Views are split out into "global" and "north-america" focused phylogenies. Available at nextstrain.org/mumps/global and nextstrain.org/mumps/north-america.
Figure 1. Phylogenetic views of mumps viral genetic diversity. Views are split out into "global" and "north-america" focused phylogenies. Available at nextstrain.org/mumps/global and nextstrain.org/mumps/north-america.
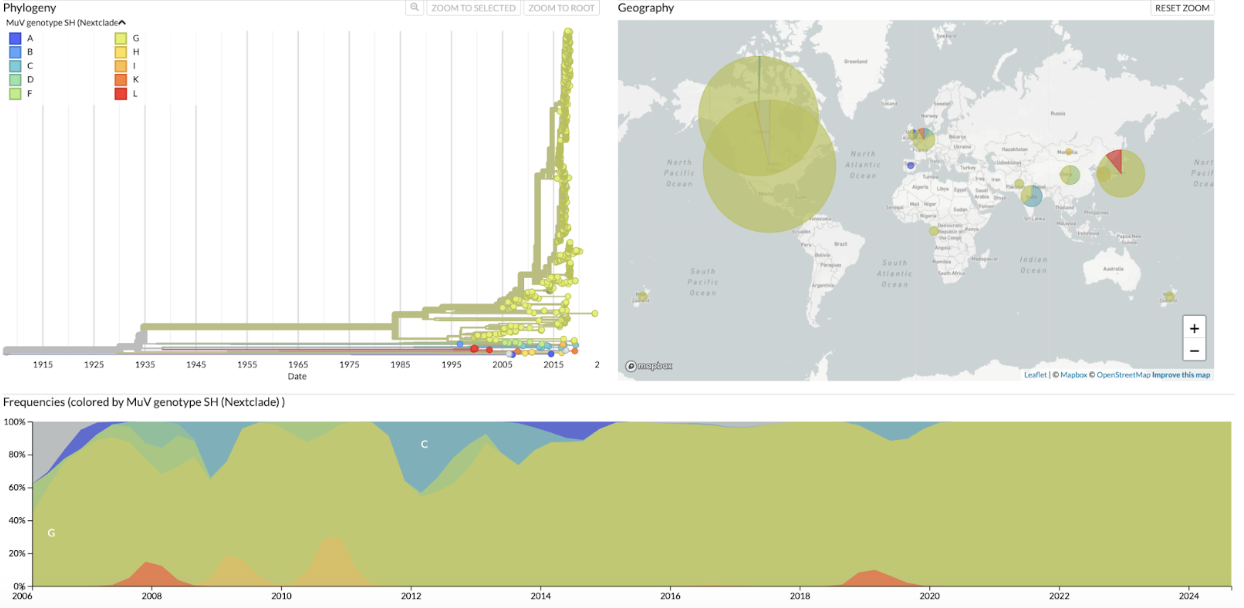 Figure 2. Annotated by Mumps genotypes. Samples are annotated by Mumps genotypes based on both GenBank annotations and Nextclade assignments. Tree, map, and frequencies plots of the mumps genome tree are shown and available at nextstrain.org/mumps/global.
Figure 2. Annotated by Mumps genotypes. Samples are annotated by Mumps genotypes based on both GenBank annotations and Nextclade assignments. Tree, map, and frequencies plots of the mumps genome tree are shown and available at nextstrain.org/mumps/global.
# Nextclade dataset
We provide two Nextclade datasets (SH region and genome) to assign genotypes (e.g. A to N) to mumps samples based on criteria outlined by the WHO and tree placement. Scaffold strains for the Nextclade dataset were pulled from the literature (Jin et al., 2005, WHO 2012, Jin et al., 2015) and augmented with some subsampling to fill in the tree. Mutations are called against a Jeryl-Lynn reference (D90232 for the SH region and HQ416907 for the full genome).
| Scope | Nextclade dataset | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SH region (~316 bp region) | mumps/sh | D90232 (Jeryl-Lynn) |
| Full genome | mumps/genome | HQ416907 (Jeryl-Lynn) |
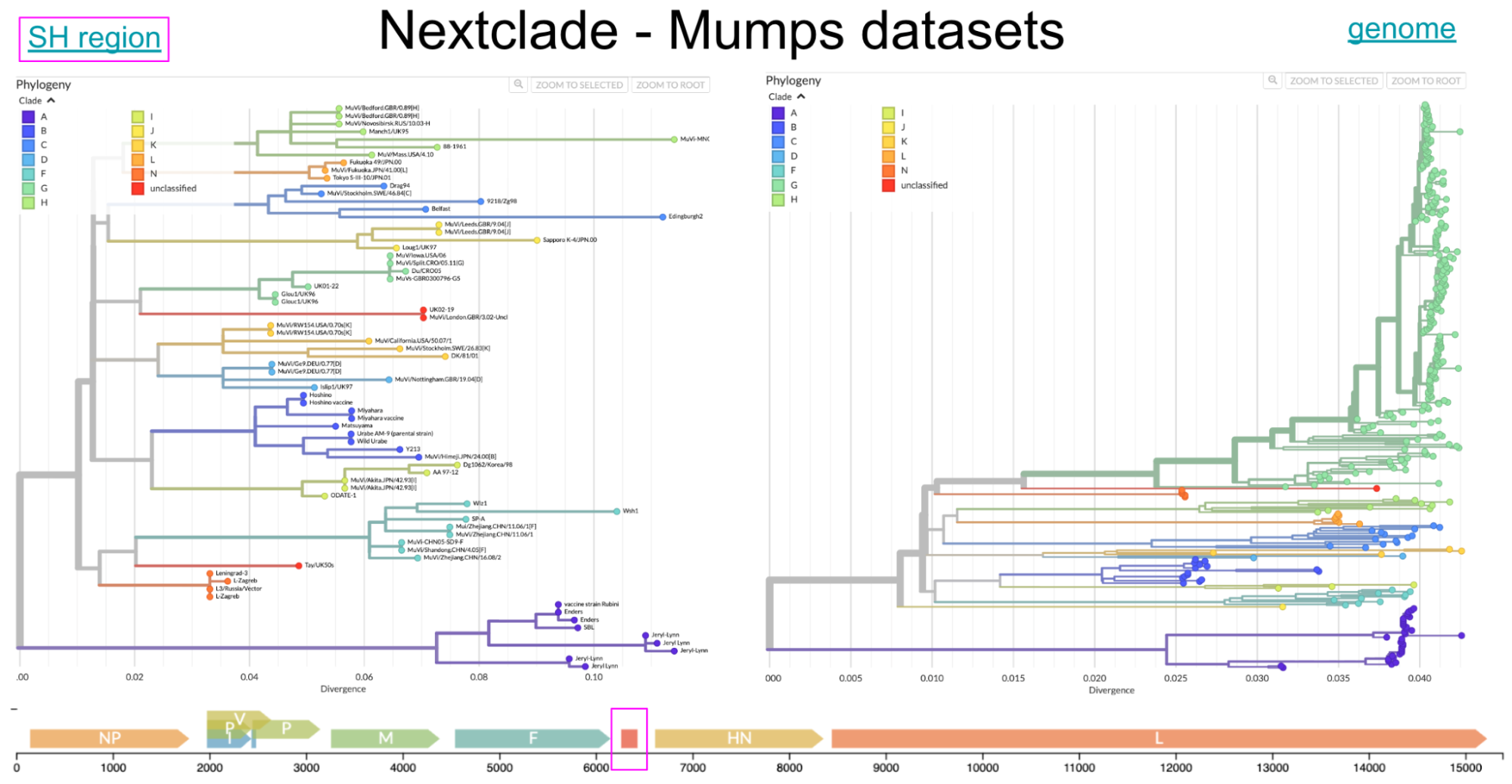 Figure 3. Nextclade datasets of mumps virus based on the ~316 SH region and the full genome. Scaffold phylogenetic trees were created for a Nextclade dataset and colored by genotype assignment. Below the trees, the SH region is highlighted in a magenta box to highlight the difference between the SH and full genome datasets. The Nextclade datasets are available as mumps/sh and mumps/genome.
Figure 3. Nextclade datasets of mumps virus based on the ~316 SH region and the full genome. Scaffold phylogenetic trees were created for a Nextclade dataset and colored by genotype assignment. Below the trees, the SH region is highlighted in a magenta box to highlight the difference between the SH and full genome datasets. The Nextclade datasets are available as mumps/sh and mumps/genome.
# Nextstrain resources
We curate sequence data and metadata from NCBI as the starting point for our analyses. Curated sequences and metadata are available as flat files at:
- data.nextstrain.org/files/workflows/mumps/metadata.tsv.zst
- data.nextstrain.org/files/workflows/mumps/sequences.fasta.zst
# Acknowledgments & request for comments
We welcome comments or suggestions from mumps researchers to improve these Nextstrain datasets for their use case. Special thanks for feedback from Louise Moncla for answering questions and providing some biological context.


















